The Concept of Natural Environment
Biotic and Abiotic Components of the Environment
Describe biotic and abiotic components of the environment
There are two components of environment;
- Biotic (living things)
- Abiotic (non living things)
BIOTIC COMPONENT
These
are living components in the environment such as animals, plants,
fungi, and microorganisms. These organisms interact together in number
of ways and these ways of interaction include the following;
- Competition, that organisms must compete for limited resources in struggle for life. For an organism to survive in an ecosystem it must compete with partner for the limited resources.
- Predation Is the system in which one organism utilize the other as food. The eater is a predator while the eaten is a prey and a number of predators and preys regulate each other
- Symbiotic relationship This is where there is a close relationship or association between organisms this association could take various forms like mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism
- Adaptation Adaptation has enabled organisms to survive. They may be anatomically structurally physiologically or behavioural. Eg some organisms are poisoners to their predator while others while others develop warming colouration
ABIOTIC COMPONENTS
These
include non living organisms that are found in ecosystem. Example air
solar, energy, soil, and nutrients. Generally abiotic components of an
ecosystem consist of physical environment and they are as follows:
- Climatic factor:Several change of climatic condition influence or determine the survival of organisms in ecosystem such condition include temperature, humidity, pressure etc
- Aquatic condition:Changes in the aquatic environment and the nature of environment it is self determined by the type of organism found in the area such a changes include water current, wave action, salinity, etc
- Light condition factor:These affect much plant population where photosynthetic process depend on the availability of light.
- Soil factor/condition:These are also adaphic factors and they include soil texture, soil structure and soil pH
Interactive of Organisms in the Environment
INTERACTION AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS
- Competition:That organisms must compete for limited resources in struggle for life. For an organism to survive in an ecosystem it must compete with partner for the limited resources .Example lions and leopards both hunt zebra, and so they are competitors
- Predation:Is the system in which one organism utilize the other as food. The eater is a predator while the eaten is a prey and a number of predators and preys regulate each other. e,g cats eat mice
- Symbiosis:This is where there is a close relationship or association between organisms this association could take various forms like mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism
- Mutualism is a relationship where two organisms benefit each other for example the rhizobium bacteria in the root nodules of legumes fix nitrogen into nitrate to be used by the plant
- Adaptation:Adaptation has enabled organisms to survive. They may be an atomically structurally physiologically or behavioural. Example some organisms are poisoners to their predator while others while others develop warming coloration
- Commensalism is the interaction that is beneficial to one organism and is neutral to the other organism. For example when a bird builds a hole or a nest in a tree
- Parasitism is the association where one organism benefit while the other is harmed. Example plasmodium that cause malaria to human
The Components of a Food Chain and Food Web
Mention the components of a food chain and food web
Producers
Are organism that can manufacture their own food for example green plants and green bacteria
Primary consumers
They are organisms that feed on producers for example rabbits, buffalo andsheep
Secondary consumer
They are organisms that feed on primary consumer
Decomposers
These organisms feed on dead matter and break it down thereby facilitating decomposition. For example bacteria and fungi
Diagrammatic Representation of a Food Chain and Food Web
Construct a diagrammatic representation of a food chain and food web
Food chain
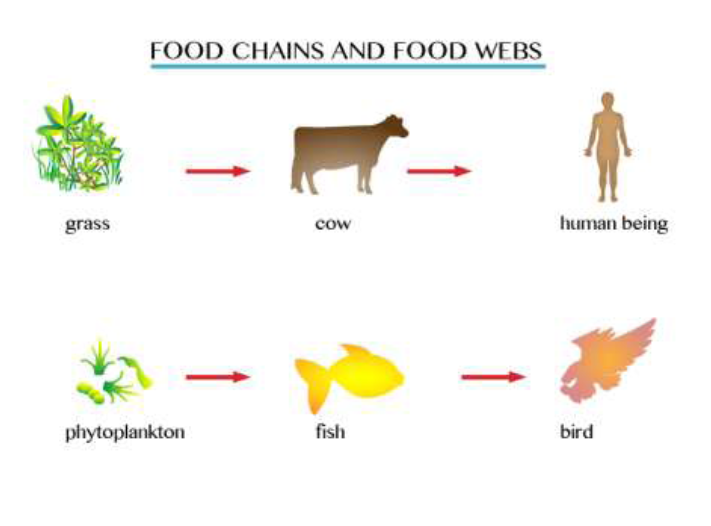
Food chain example
- Grass →cow→human being
- Phytoplankton→fish→bird
Food web
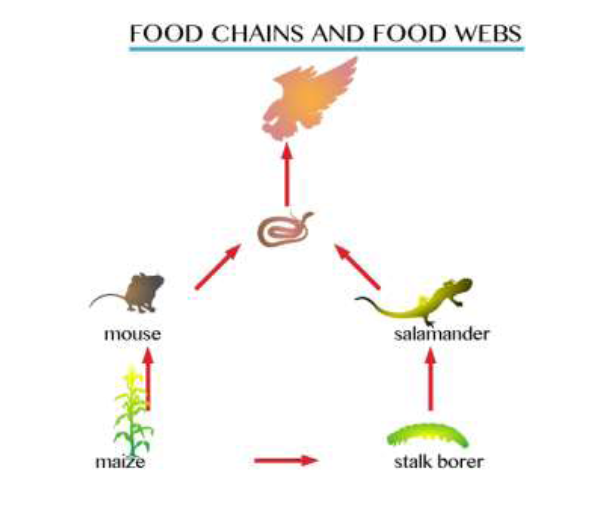
The Significance of Food Chain and Food Web in Real Life Situation
Explain the significance of food chain and food web in real life situation
The following are the significant of food chain and food web
- Food chains and webs help in the flow of energy from producers to consumers and from one trophic level to another, without which energy flow would be impossible.
- Food chain studies have had an important role in ecotoxicology studies tracing path ways and biomagnifications of environmental contaminants.
- Learning how the food chain works enable us to understand the importance living organisms that make up the food chain and how the ecology is balanced. This is crucial since any interruption in food chain could lead to ecosystem imbalance.
- Food chains and webs show the flow of energy through an ecosystem.
- Understanding the effect of polluting the natural environment enable us to avoid or control environmental pollution so as to maintain natural ecosystems.




