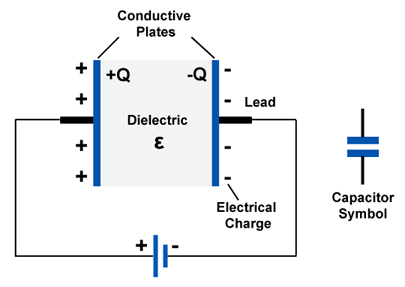
The Action of a Capacitor
Capacitor
is a device which is used for the storage of charges consisting of two
conductors, parallel-nearly separated by air or any other dielectric.Dielectric is an insulating medium used between plates of a capacitor.
Mode of Action of a Capacitance
Explain mode of action of a capacitance
The
capacitor store energy by keeping electrical charges on its plates.
Capacitors are used in radio circuits, television circuits and other
electronic devices.
When
the power switches off, the energy stored in the plates of the
capacitor will be released to flow in the circuit for sometimes. This
will keep the device functioning until all the energy is worn out.
That
means, when the electric power is available, the capacitor is charged
and store electric energy on its plates but when the power in the
circuit switches OFF, the capacitor continues to supply the electrical
power in the circuit. This process through which the capacitor releases
its charges to the circuit is known as discharging.
The Action of a Capacitor
Explain the action of a capacitor
A
fully charged capacitor has a net positive charge on one of its plates
and a net negative charge on the other plate. The potential difference
between its plates can be measured by connecting the voltmeter across
its plates.
The
ability of a capacitor to store charges is known as the capacitance.
Capacitance is the ratio between the quantity of charge stored and the
potential difference (p.d) across the plates of the capacitor.
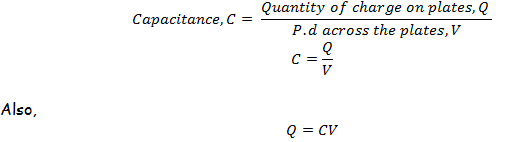
That means, the quantity of charges Q increases with the increase in the potential difference (p.d) across the plates.
The S.I unit of capacitance is is Farads (F). Other units include microfarads (µF), picofarads (Pf) and nanoFarads (nF).
A farad is the capacitance of a conductor that its potential difference can be changed by 1 volt by a charge of 1 coulomb.
However,
1 Farad capacitance is very large to be reached thus most of the times
the smaller units are used to simplify measurements.
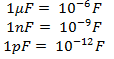
Example 1
A 3µF capacitor has a 18V of potential difference. What will be its total charge?
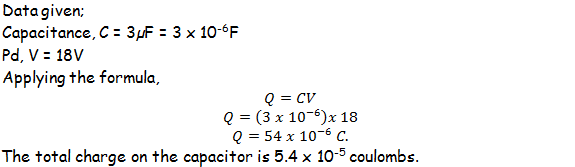
Example 2
Calculate the capacitance of the capacitor if the cell connected to it has 1.5V when the charge is 120 coulombs.
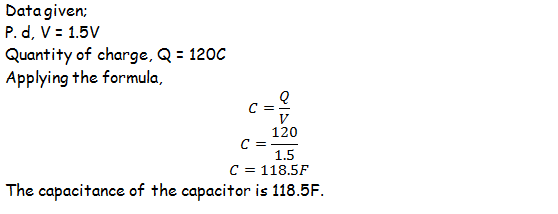
Construction of an Air-filled Capacitor
Describe the construction of an air-filled capacitor
This
constitute two parallel metal plates with air band between them.A flat
metal A is set up vertically on insulating legs and is connected to a
gold leaf electroscope by means of a wire.
The
plate is then given a positive charge by induction with a negatively
charged ebonite rod. The divergence of the leaf indicates the potential
of the plate.A second insulated plate B is now brought up slowly into a
position parallel to A.
When
B is very close to A but not touching it, it will be noticed that the
leaf divergence decreases very slightly.We conclude from this that the
potential of A has been decreased by the presence of B, and hence its
capacitance has increased slightly.
Equivalence Capacitance of a Combination of Capacitors
Determine equivalence capacitance of a combination of capacitors
Factors affecting the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor.
There are three factors which affect the capacitance of a parallel-plate capacitor, namely;
- Area of plates
- Distance apart of the plates.
- Dielectric between the plates.
Relative permeability (dielectric constant) of a medium
Relative permeability
is the ratio of the capacitance of a given capacitor with the medium as
dielectric to the capacitance of the capacitor with a vacuum as the
dielectric.
It
has no units since it is a ration of similar quantities.Paraffin wax
has a relative permeability of about 2 while that of mica is about 8.
Combination of capacitors
Capacitors can be combined in series or in parallel so as to prevent overheating by being continuously overcharged.
Capacitors in Series.
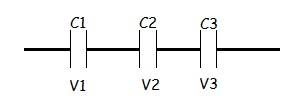
When capacitors are in series, charge distribution Q is equal to all capacitors but p.d, V and capacitance are different.
Therefore, the total p.d, VT
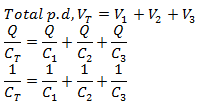
Where, CT is the equivalent capacitance (combined capacitance) for the capacitors in series.
Capacitors in Parallel.
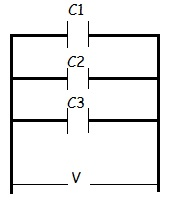
When capacitors are in parallel, potential difference V is equal to all capacitors but charge distribution, Q and capacitance are different.
Therefore, the total charge, QT
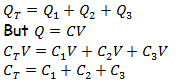
Where by, CT is the equivalent capacitance (combined capacitance) for capacitors in parallel.




