OPTICAL INSTRUMENT
The Structure of the Human Eye
Describe the structure of the human eye
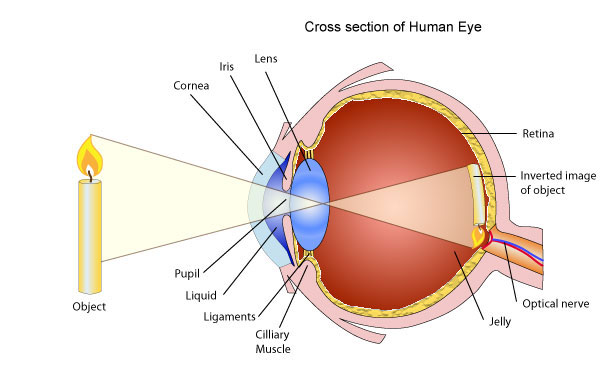
The eyeball approximately spherical in shape.The wall of this sphere consist of two layers, the outer layer or sclera and the inner layer or choroid.The front portion of the SCLERA FORMS A TRANSPARENT CURVED section called the camera.The choroid layer is balance in order to prevent internal reflection and also to protect the light sensitive parts of the eye.
The aqueous and vitreous hum our are jelly – like substance that fills the spaces within the eyeball.The aqueous humour is the salt solution of refractive index n, 1.38.Vitrous hurmour is a watery , Jelly substance of refractive index 1.34.Behind the cornea there is a colored diagram called the iris.
The iris has the central hole called the pupil. The iris contains muscles which control the size of the pupil. The size of the pupil decreased in the bright light and increased in the dim light.
Behind the pupil and there is a crystalline lens held in position by suspensory ligaments that are attached to the choroid layer.Near the suspensory ligaments are the ciliary muscles.The function of the suspensor ligaments there are the cilliary muscles.
The function of cillary muscles is to control the thickness of the lens. The lens become thick when the ciliary muscles contract and thin when the ciliary muscles are relaxed.
<!--[endif]-->At the back of the eye there is a retina (This is the part of the eye which is sensitive to light).Image formed is inverted formed on the Retina ( This is the part of the eye which is sensitive to light.)
Image formed is inverted formed on the retina by successive refraction of light at the corner, the aqueous hurmour the crystalline lens and the Vitreous hurmour.Electrical signals are then transmitted to the Brain through the topic nerve. Finally, the brain interprets these signals.
Accommodation Power of the Human Eye
Explain accommodation power of the human eye
Accommodation is the process whereby the eye alters its focal length in order to form images of objects at different distances.
(Thickening or Thinning of the lens causes a change in its focal length).
The thickening or thinning of the crystalline lens is made possible by the action of the ciliary muscles.To view neare object t, ciliuary muscles contract, this makes the lens thicker.
In the relaxed state of ciliary muscles, the crystalline lens become thinner and enables the eye to see (view) distant objects. The farthest point which can be seen clearly is called the far point of the eye and the nearest point is called the near point of the eye.
The corresponding distance from these points to the eye are referred to as the maximum and least distance of district vision respectively.A normal eye (i.e. without defects of vision) has a far point at infinity and near point at a distance of 25cm from the eye.Structure of lens “ view distant object”
The Defects of the Human Eye
Identify the defects of the human eye
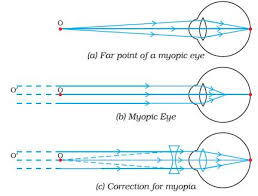
Myopia or near-sightedness
- This defect causes person to see near object clearly while distant objects are not seen clearly.
- The strength of the cornea and the eye lens combination is too great even when muscles of the eye are completely relaxed.
- The focal length of the cornea and the eye – lens combination is always less than the distance to the retina.
- Images of distant object are formed in front of the retina even when eye is totally relaxed. However, an object that is closer can be brought into focus.
- In this situation the focal length of the cornea and the eye lens is so short that objects closer than the conventional (near point of 25cm) can be brought into focus. That’s why this condition is called Short sightedness (near sightedness).
- Since the problem is that the strength of the eye – lens and the cornea combination is too great, the solution is to provide eye glasses (or contract lenses) with negative lens.
- The negative lens weakens the strength of the cornea and eye – lens just enough so that the resulting focal length when the eye muscles are relaxed matches the distance back to the retina so that distant images are now in focused.
- The eye glass lenses are negative lenses that means they are thinner in the middle than at the edges.
- It is easy to identify this kind of eye glass lenses since acting by themselves they do not form a real image of an object at any distance.
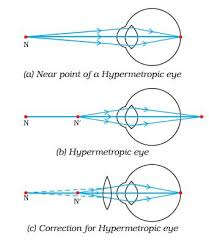
Hyperopia or far-sightedness
- This defect causes a person to see distant objects only and short-distance objects are not seen clearly.
- In the person with this condition, the strength of the cornea and the eye-lens combination is too weak when the eye muscles are totally relaxed. So the image of a distant object is formed behind the retina.
- The solution in the opposite of myopia. Victims should wear positive eye lenses which strengthen the corner and the eye lens just enough so that the resulting focal length when the eye is relaxed matches the distance to the back of the retina.
Astigmatism
- This occurs when the focal length for the cornea and the eye's lens for an object oriented in some direction is not the same as for another located in a perpendicular direction.
- The eye can not bring the vertical and horizontal lines in a ‘+’ symbol in sharp focus at the same time. (The axis of differing focal length need not be exactly horizontal and vertical).
- The problem is that the cornea of the eye lens is not symmetrical. The solution is to use eye glasses whose lenses are not symmetrical in a complementary way.
- The cylindrical lens may be combined with an additional positive or negative lenses.
<!-- [if gte mso 9]><xml> Normal 0 false false false EN-US X-NONE X-NONE MicrosoftInternetExplorer4 </xml><![endif]--> Decreased accommodation
- This condition typically occurs in middle-aged people.
- The eye muscles gradually weaken with age, so that the range or accommodation is decreased.
- People with this condition cannot bring both near objects and far objects into focus.
- The weakening of the eye muscles often causes the focal length of the eye lens to increase as well so that many people of middle age tend to become far sighted.
- Since the problem is adequate accommodation, no single lens can correct it and people with this problem usual needs bifocals.
- Bifocals are glasses with two different lens strengths, one for near and one for distant objects.
- The usual arrangement is that the bottom half of the lens is the near strength and the top half is the far strength.
The Correction of the Defects of Human Eye
Describe the correction of the defects of human eye
Myopia is common name for impaired vision in which a person sees near objects clearly while distant objects appear blurred. In such a defective eye, the image of a distantobject is formed in front of the retina and not at the retina itself. Consequently, a nearsighted person cannot focus clearly on an object farther away thanthe far point for the defective eye.
This defect arises because the power of the eye is too great due to the decrease in focal length of the crystalline lens. This may arise due to either
- excessive curvature of the cornea, or
- elongation of the eyeball.
Correction:Thisdefectcan becorrectedby using aconcave (diverging) lens. A concave lens of appropriate power or focal length is able to bring the image of the object back on the retina itself.
Farsightedness, also called hypermetropia, common name for a defect in vision in which a person sees near objects with blurred vision, while distant objects appear in sharp focus. In this case, the image is formed behind the retina.
This defect arises because either
- the focal length of the eyelens is too great, or
- the eyeball becomes too short, so that light rays from the nearby object, say at point N, cannot be brought to focus on the retina to give a distinct image.
Correction:This defect can be corrected by using aconvex(converging) lensof appropriate focal length. When the object is at N’, the eye exerts its maximum power of accommodation. Eyeglasses with converginglenses supply the additional focussing power required for forming the image on the retina.
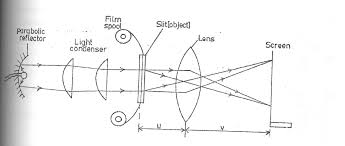
The Human Eye and the Lens Camera
Compare the human eye and the lens camera
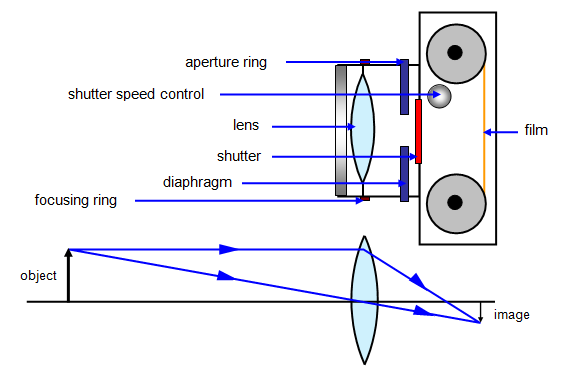
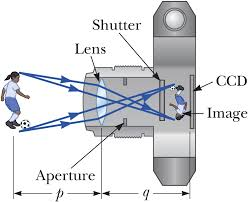
The camera
- The eye and the camera has a have a convex lens which form a real and inverted image of an object.
- The eye and the camera are blackened inside to prevent internal reflection. Rays of light which are not received on the retina or camera film are absorbed by the choroid layer of the eye or the black surface inside the camera.
- The eye can regulate the amount of light that passes through the crystalline lens by using pupil while in a camera the diaphragm regulates light.
- In the eye the image is formed in the retina while in the camera the image is formed on the photographic plate.
- The eye can change the focal length of its lens by the contraction and relaxation of the ciliary muscles. In this way the eye can focus objects at different distance. In a camera objects at different distance are focused on by moving the lens forwards and backwards.