BALANCE OF NATURE
The Natural Environment
The Concept of Natural Environment
Explain the concept of natural environment
Natural environment is made up of all living and non living things that occur naturally on earth. An organism living anywhere in any environment is affected by the things around it such as air, water, animals, plants, microorganism, stones, rock, soil, clouds and the sun. everything around it in fact makes its natural environment. It is important to understand that the environment includes all living things as well as non living things.
IMPORTANT TERMS
- Ecology: is the branch of biology that deals with studying interaction oforganisms with their environment
- Population: is the total number of organisms of the same species living in a certain area. Example the number of frogs in a pond
- Community: this refers to the sum of total of all population of different organisms living in a specific called habitat
- Habitat: is the specific area where an organism is found and adopted. i.e it is an appropriate for the certain community example an ocean, grassland, and a pond
- Ecosystem: refers to a natural unit made up of living and non living things whose interaction
Biotic and Abiotic Components of the Environment
Describe biotic and abiotic components of the environment
There are two components of environment,;
- Biotic (living things)
- Abiotic (non living things)
BIOTIC COMPONENT
These are living components in the environment such as animals, plants, fungi, andmicroorganisms. These organisms interact together in number of ways and these waysof interaction include the following;
- Competition That organisms must compete for limited resources in struggle for life. For anorganism to survive in an ecosystem it must compete with partner for thelimited resources.
- Predation Is the system in which one organism utilize the other as food. The eater is a predator while the eaten is a prey and a number of predators and preysregulate each other
- Symbiotic relationship This is where there is a close relationship or association between organism sthis association could take various forms like mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism
- Adaptation Adaptation has enabled organisms to survive. They may be anatomically structurally physiologically or behavioral. Eg some organisms are poisoners totheir predator while others while others develop warming colouration
ABIOTIC COMPONENTS
These include non living organisms that are found in ecosystem. Example air solar,energy, soil, and nutrients. Generally abiotic components of an ecosystem consist ofphysical environment and they are as follows.
- Climatic factor Several change of climatic condition influence or determine the survival of organisms in ecosystem such condition include temperature, humidity,pressure etc
- Aquatic condition Changes in the aquatic environment and the nature of environment it is self determined by the type of organism found in the area such a changes include water current, wave action, salinity, etc
- Light condition factor These affect much plant population where photosynthetic process depend onthe availability of light.
- Soil factor/conditionThese are also adaphic factors and they include soil texture, soil structure and soil PH
Various Organism in their Natural Environment in the Community
Identify various organism in their natural environment in the community
Activity 1
Identify various organism in their natural environment in the community
The Importance of the Natural Environment
Explain the importance of the natural environment
IMPORTANCE OF NATURAL ENVIRONMENT
- It is a source of food to organisms
- It provides shelter and security for organisms
- It allow living and non living things to interact
- It provides an appropriate setting for organisms to reproduce andincrease in number.
Interactive of Organisms in the Environment
Ways in Which Living Organisms Interact with the Non Living Component of the Environment
Identify ways in which living organisms interact with the non living component of the environment
The following are the interaction of organism in the environment
- Ground water and water from rain flow into streams and rivers
- The stream and rivers flow into lakes and ocean
- Water evaporate into the atmosphere from lakes and ocean and from plantsthrough transpiration
- The evaporated water precipitates to form water vapor which condenses toform clouds
- Wind causes clouds to move for example from above the ocean to above theland
- Rain fall and absorbed by plants or form grounds water, and the cycle beginsagain..
The Interaction of Organisms among Themselves
Explain the interaction of organisms among themselves
INTERACTION AMONG LIVING ORGANISMS
- CompetitionThat organisms must compete for limited resources in struggle for life. For anorganism to survive in an ecosystem it must compete with partner for thelimited resources .EXAMPLE lions and leopards both hunt zebra, and so theyare competitors
- PredationIs the system in which one organism utilize the other as food. The eater is apredator while the eaten is a prey and a number of predators and preysregulate each other. e,g cats eat mice
- SymbiosisThis is where there is a close relationship or association between organismsthis association could take various forms like mutualism, commensalism, andparasitism
- Mutualism is a relationship where two organisms benefit each other forexample the rhizobium bacteria in the root nodules of legumes fix nitrogeninto nitrate to ne used by the plant
- AdaptationAdaptation has enabled organisms to survive. They may be anatomicallystructurally physiologically or behavioral. Eg some organisms are poisoners totheir predator while others while others develop warming coloration
- Commensalism is the interaction that is beneficial to one organism and isneutral to the other organism. For example when a bird builds a hole or a nestin a tree
- Parasitism is the association where one organism benefit while the other isharmed. E.g plasmodium that cause malaria to human
Food Chain and Food Web
The Meaning of Food Chain and Food Web
Explain the meaning of food chain and food web
FOOD CHAIN
Is the sequence of living things in which each organism is the food of the next in thesequence.
- 1. Grass →Zebra→Lion
- Maize plant→grasshoppe→rFrog
→
FOOD WEB
Is made of interconnecting food chains
The Components of a Food Chain and Food Web
Mention the components of a food chain and food web
Producers
Are organism that can manufacture their own food for example green plantsand green bacteria
Primary consumers
They are organisms that feed on producers for example rabbits, buffalo andsheep
Secondary consumer
They are organisms that feed on primary consumer
Decomposers
These organisms feed on dead matter and break it down thereby facilitatingdecomposition. For example bacteria and fungi
The Difference between Food Chain and Food Web
Distinguish food chain from food web
Differences between food chain and food web
| Food chain | Food web |
| 1. It consists of the single straight pathwaythrough which food energy travels in an ecosystem | 1. It consists of a number of interconnectedfood chains through which energy travelsin an ecosystem |
| 2. Usually members of the higher trophiclevel feed upon a single type of organismsof lower trophic level | 2. Usually members of the higher trophiclevel feed upon many organisms of lowertrophic level |
| 3. Isolated or separate food chainsincreases the instability of the ecosystem | 3. Presence of complex food websincreases the stability of the ecosystem |
| 4. It does not have any effect on improvingthe adaptability and competitiveness of theorganisms | 4. More complex food webs improves theadaptability and competitiveness of theorganisms |
Diagrammatic Representation of a Food Chain and Food Web
Construct a diagrammatic representation of a food chain and food web
Food chain
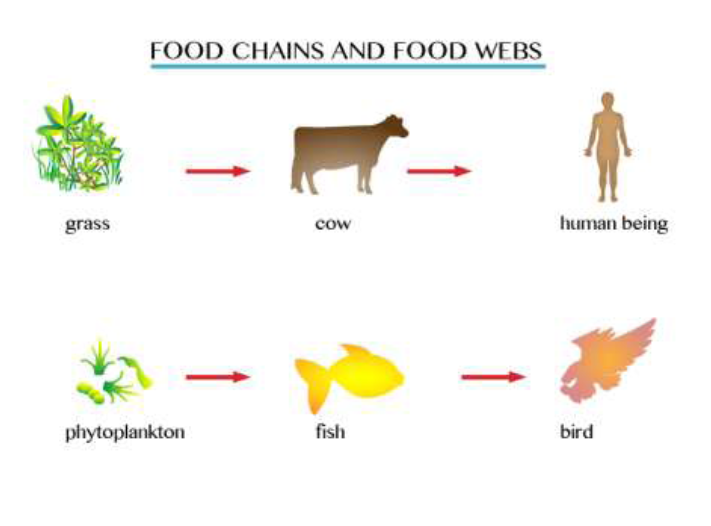
Food chain example
- Grass →cow→human being
- Phytoplankton→fish→bird
Food web
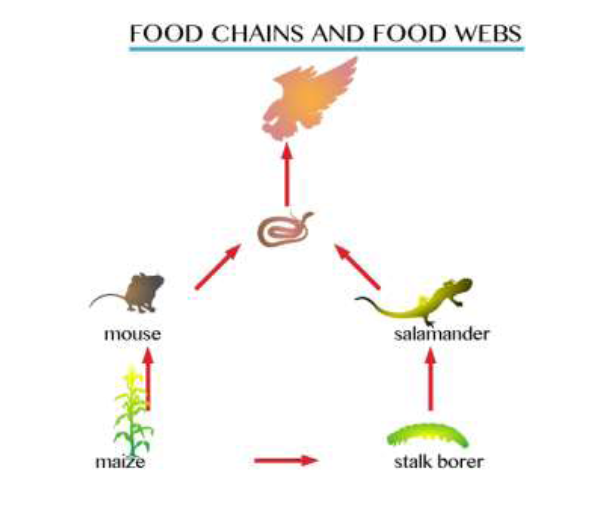
The Significance of Food Chain and Food Web in Real Life Situation
Explain the significance of food chain and food web in real life situation
The following are the significant of food chain and food web
- Food chains and webs help in the flow of energy from producers to consumers andfrom one trophic level to another, without which energy flow would be impossible.
- Food chain studies have had an important role in ecotoxicology studies tracingpathways and biomagnifications of environmental contaminants.
- Learning how the food chain works enable us to understand the importance livingorganisms that make up the food chain and how the ecology is balanced. This iscrucial since any interruption in food chain could lead to ecosystem imbalance.
- Food chains and webs show the flow of energy through an ecosystem.
- Understanding the effect of polluting the natural environment enable us to avoid orcontrol environmental pollution so as to maintain natural ecosystems.




