HARDNESS OF WATER
The Concept of Hardness of Water
As water flows over the land, it dissolves many mineral substances. The
dissolved minerals are deposited together with water in rivers, lakes and
oceans. Water is said to be hard if it contains some specific type of dissolved
minerals. It is important to note that not all dissolved salts make water hard.
As you learned early, water is treated in water purification plants
before being piped to your home. The treatment removes only the insoluble
particles and kills bacteria. So the water still is not pure. It contains
natural compounds dissolved from rocks and soil. It may also contain traces of
chemicals dumped from homes, farms and factories.
Water obtained from an area where the rocks contains chalk, limestone,
dolomite or gypsum, contains dissolved calcium and magnesium sulphates and hydrogencarbonates.
These salts make the water hard.
One can distinguish between hard and soft water when washing with soap.
Hard water does not form lather easily. Instead, it forms a precipitate or
scum. It requires much soap to react with all the dissolved minerals before
enough lather is formed. Therefore, hard water wastes soap during washing.
When soap is used with hard water a “scum” forms on the surface. This is
a result of a precipitation reaction between calcium and/or magnesium ions and
soap. Soaps are the sodium or potassium salts of long-chain organic acids.
Soaps are made from animal fats by treatment with alkali (NaOH or KOH).
Ordinary washing soap is a compound of stearic acid, C17H35COOH. Thenature of such soaps is
the salt, sodium stearate, C17H35COONa+. Sodium stearate is soluble in water but calcium stearate is not.
When soap is mixed with hard water, the calcium or magnesium salts in
the hard water react with soap and precipitates as scum. The nature of scum is
either calcium stearate or magnesium stearate:
Soap will not form any lather with water until all the calcium and
magnesium ions have been precipitated. Hard water, therefore, wastes soap. This
means that more soap may be used for an efficient washing. The amount of soap
needed to just produce froth can be used to estimate the hardness of water.
The problem of scum formation only occurs with soaps. Soapless
detergents do not produce scum. The trade names for some soapy detergents sold
in Tanzania include Komoa, Kuku, Taifa,
Mbuni, Mshindi, Changu, Jamaa and
several other bar soaps. The trade names for some soapless detergents include Omo,
Foma, Tesa, Toss, Dynamo, Swan.
CAUSES OF WATER HARDNESS
Do you live in an area with
hard water? If you do, you will be used to the scum that forms when you
use soap in the water.
In this unit you can find out what hard water is, how it
forms, its effects, and how we can remove hardness from water. Water is generally said to be hard if it contains soluble salts of
calcium and magnesium. The salts are calcium and magnesium sulphates and
hydrogencarbonates. Hardness of water is caused by higher than usual levels of
calcium (Ca2+) and magnesium (Mg2+) ions in water.
As rain water passes through the atmosphere, it dissolves carbondioxide
to form a weak carbonic acid.
As
this solution passes over and through rocks containing chalk, limestone
or dolomite, the rainwater very slowly dissolves them:
H2CO3(aq) + CaCO3(s) → Ca(HCO3)2 (aq)
The calcium hydrogencarbonate formed is soluble in water and is responsible for the presence of calcium (Ca2+) ions in water.
Interpretation of the results
From
the result of experiment, we can conclude that scum is produced when
either calcium or magnesium salt is present in water. So, high levels of
calcium or magnesium ions in water are responsible for water hardness.
When the concentration of either of these minerals is over 150 milligrams per cubic decimeter (150 mg/dm3), water is considered to be hard. The upper limit allowed is 300 mg/dm3
The
hard water in some areas can be softened simply by boiling the water,
but this is not true in all cases. This means that the hardness in water
can be divided into two types – temporary and permanent hardness.
Temporary hardness
Temporary
hardness in water is caused by dissolved calcium or magnesium
hydrogencarbonates. The most important characteristic of temporarily
hard water is that it can be softened by simply boiling. When the water
is boiled, the soluble sodium hydrogencarbonate is decomposed to form
the insoluble calcium carbonate.
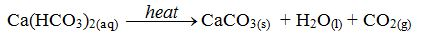
The
decomposition causes the “furring” of kettles, hot water pipes and
shower heads. This means that the inside of kettles, pipes and shower
heads become coated with a layer of calcium carbonate (limescale) caused by the decomposition of the hydrogen carbonate according to the equation above.
In
many supermarkets, it is possible to buy a limescale remover. This is
often a solution of methanoic acid (formic acid). This weak acid is
strong enough to react with limescale but not with the metal. The
insoluble limescale (carbonate) is probably dissolved to a soluble
compound, calcium methanoate that can be flushed away with water.
2COOH(aq) + CaCO3(s)(insoluble)→ Ca(HCOO)2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)calcium methanoate (soluble)
Permanent hardness
Permanent hardness in water is caused by soluble sulphates and chlorides of calcium and magnesium (CaSO4, MgSO4, CaCl2 and MgCl2).
This type of hardness cannot be removed by boiling the water. This is
because boiling does not decompose the chlorides of calcium or
magnesium. Such water may only be softened by chemical treatment or ion
exchange methods
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN SOFT AND HARD WATER
When calcium carbonate is reacted with dilute hydrochloric acid, carbon dioxide gas is produced.
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
When
carbon dioxide gas is bubbled through a suspension of calcium carbonate
in water for a long time, the insoluble calcium carbonate dissolves to
give the soluble bicarbonate, the presence of which makes the water
hard.
CO2(g) + CaCO3(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(HCO3)2(aq)
The
purpose of heating solutions in test tubes M and P was to try to remove
water hardness. However, only the hardness in test tube M was merely
removed by boiling because it contains the temporarily hard water.
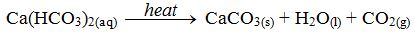
The
hardness in test tube P could not be removed by just boiling because it
contained the hard water. Calcium chloride cannot be decomposed by
heat. So, no change is expected after heating.
Results:
- Scum was formed in test tubes N, P and Q but P and Q contained more scum than N.
- Lather was formed in test tube M only.
- Test tube M contained temporarily hard water and test tube P contained permanently hard water. The hardness in test tube M was removed by boiling while that in test tube P was not.
- Test tubes P and Q contained permanently hard water. The hardness in this water could not be removed by mere boiling.
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGE OF HARD WATER
There are advantages and disadvantages for people who live in hard water areas. Look at the table below:
|
CONCEPT OF SOFT WATER
Basicallly we have two types of water namely: hard and soft water. The concept of hard water has been covered, what I want to do here is to give you a brief concept of soft water.
SOFT WATER is that water which can easily form leathers with soap. In short soft water have no chemical components like magnessium and calcium that may cause water hardness
Soft water have both advantages and disadvantages, there is one saying "huwezi chinja mbuzi akakosa mifupa"
The advantages of soft water
- Since soft water lathers easily with soap, it helps in saving a lot of soap when used in washing. It is therefore economical to use soft water in washing.
- It is compatible with dyeing, which is why the dyeing industry prefers using it in their business.
- It does not stain white clothes when used in laundry, unlike hard water does.
- Unlike the hard water, soft water does not form scales in kettles or pipes when it stays long in these containers.
- Soft water can easily lead to lead poisoning if it is transferred through lead pipes or kept in lead containers. This is possible because it can quickly dissolve lead.
- Soft water does not help in strengthening our bones and teeth since it contains no calcium.
- Soft water has a taste which is not pleasant in the mouth. Hard water, on the other hand, has a very pleasant taste.
- Soft water is not very safe for drinking as compared to hard water.







